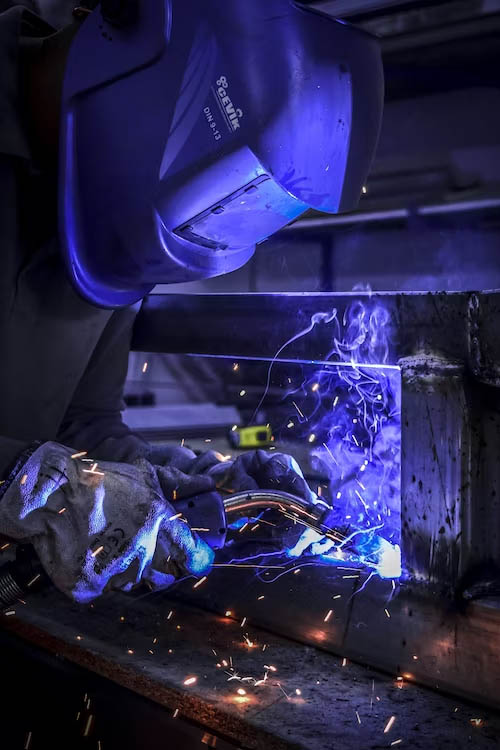
In today’s manufacturing world, welding is a standard fabrication process. There are many types of welding processes, of which the MIG and the TIG welding processes are popular and frequently used.
There has been a lot of debate between the TIG and the MIG welding for a long time. In this article, we will present some facts to unfold the ultimate particulars on this topic.
MIG vs TIG Welding
Welding Town
What Is The Basic Principle Of The Welding Process?
If we put it in simple terms, welding creates a durable joint between two metals. There are many types of processes involved in creating the joining or connection.
The basic theory behind creating this bond through welding is inducing extreme heat and pressure at the objects’ joining point. The intense heat and pressure melt the metals and solidifies to make the connection.
While some of the welding processes use either heat or pressure, but in other methods, both parameters are utilized simultaneously to complete the joining.
What Are MIG And TIG Welding?
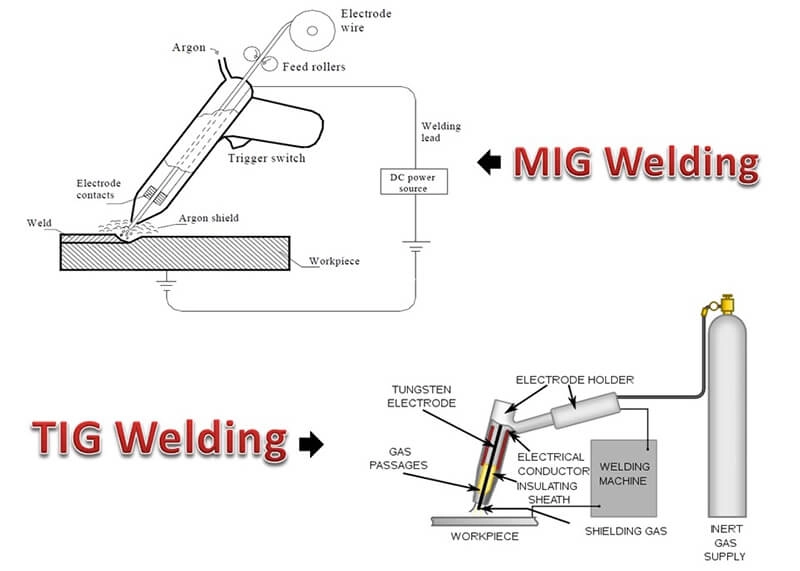
The MIG and the TIG are two types of welding processes used to join metal workpieces. If you are experienced in welding operations to some extent, you might have heard of MIG welding more frequently than TIG welding. But what do these acronyms mean?

MIG stands for metal inert gas. The MIG welding process is moderately a straightforward process in comparison to other welding techniques. During the process, the machine-fed consumable electrode is melted at the connection point.
The molten material creates an artificial arc surrounding the joint. This molten metal acts as the filler material. Once the molten material solidifies, a durable joint is formed between the metals.
TIG is an acronym that stands for tungsten inert gas. TIG welding involves a more complicated procedure compared to the MIG welding process. The electrode inside the welding gun is made of tungsten.
When you are performing the TIG welding, the non-consumable electrode passes the electricity to the joining surface. It melts the surface of the joining materials to create the arc. Once it solidifies, your desired connection is made.
MIG Vs TIG – Which Is Better?
Both the MIG and the TIG are better options in respect to the specific application. Many novices are quick to conclude that MIG is better since most people are frequently involved with MIG welding due to its simplicity.
For some particular cases, the MIG welding could prove to be the better alternative. For example, if you are looking to weld on workpieces that are very thick and require quick action, you better choose MIG welding.
Again, for specific cases, the TIG welding could prove beneficial for working on weldments composed of comparatively thinner sections requiring a quality output.
So, depending on the case scenario and what kind of target you want to achieve, the specific welding procedure will prove to be the better and efficient option for you.
You can learn more about TIG and MIG welding from the following video.
How Does The MIG And TIG Welding Processes Work?
The basic progression involved with the MIG and the TIG welding processes is very much alike. Both the MIG and the TIG are categorized within arc welding processes.
- Arc welding: When electricity is passed through the welding gun, excessive heat and pressure are generated at the concerning points between the conducting rod and the base materials. This melts the surface metals to create an arc. The melted metal later solidifies to create the bond.
- Electrode function and arc formation in MIG and TIG welding: If you perform MIG welding operation, the arc will be created when an electric current is conducted through an electrode coming of the weld-torch gun you are operating. The electrode gets consumed in the process.
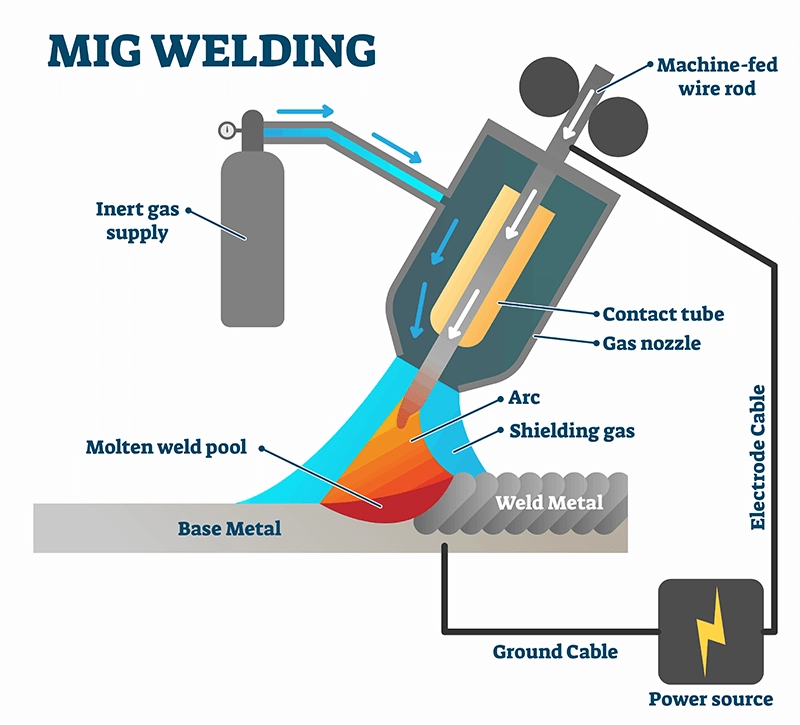
The arc’s area of effect is large, resulting in the spreading of wide weld spatter. Although the heat generated is very high, since the heat is evenly distributed over the large area, you can induce less depth of penetration due to less intensity.
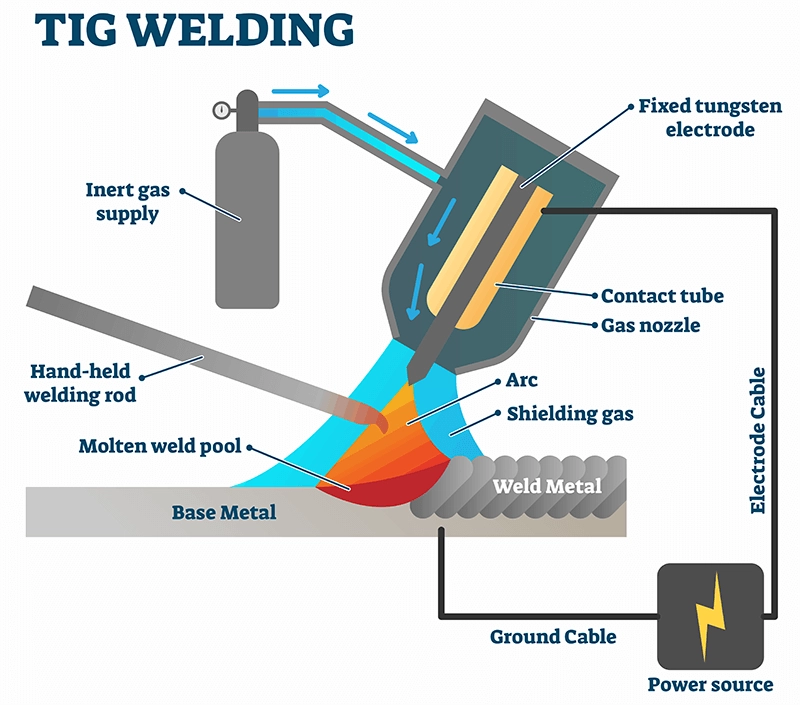
If you perform TIG welding, the arc is created between the electrode that remains stationary within the torch. The electrode is made from tungsten that does not wear off if you use it properly.
The area of effect for weld spatter is also narrower. Due to the excessive heat generated in smaller areas, the intensity of heat magnifies to penetrate deeper.
- Filler wire feed: Performing TIG welding is a comparatively complex procedure because you have to manually hold the wire at the weld pool to feed the filler. But in MIG welding, the consumable filler wire is automatically fed from the electrode feeding from a spool inside the machine.
- Shielding gas supply: It is necessary to protect the just-made melted weld bead from Oxidation reaction due to the presence of oxygen in the air. So, a shielding gas is supplied manually at the connection points to protect the newly formed beads.
For both MIG and TIG welding, the shielding gas is constituted of inert gas. Due to the non-reactive nature of the inert gas, it does not react with the weld bead. Moreover, it protects the weld bead from reaction with exterior weather for a short instance.
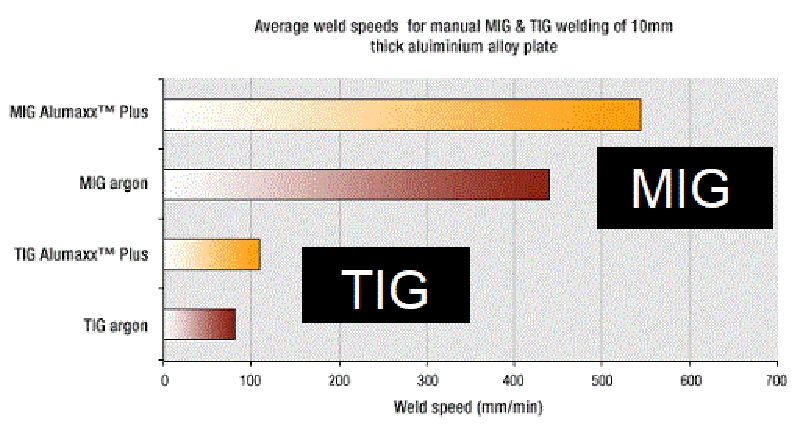
MIG Vs TIG – Which Process Is Faster?
Given the simplicity of operation, it is evident that the MIG welding process is much quicker compared to the TIG welding process.
It’s pretty fast to set up the MIG welding platform since all the processes are automatically done within the machine. You need to insert the filler wire feed within the spool inside the machine.
During the welding operation, the machine automatically rolls the spooler at a fixed pace to balance the amount of wire required to be filled. Due to this feature, you can quickly perform long continuous welding operations on pipe perimeters, longitudinal sections, or other application fields.
But there is one crucial concern you must consider while performing MIG welding on long continuous welds. As mentioned earlier, due to the large area of effect, the intensity and penetration depth is lower. You should not try to exceed optimum speed, as it might result in less penetration depth, spoiling the minimum weld quality.
On the other hand, while performing TIG welding operations, you have to feed the filler wire with another hand manually. You have to give the optimum amount of time to feed and melt the filler material.
So, to obtain the necessary results, you have to give sufficient time at each connection point to reach the desired penetration level.
In summary, MIG welding is much quicker than TIG welding. Some results show that you can even reduce the welding time to half by the MIG welding technique.
Do I Need To Extensively Train My Welder For MIG Or TIG Welding Operations?
Compared to MIG, TIG welding is more challenging and complex in the process. If your business is involved in welding operations where you need to ensure higher quality by TIG welding, it is essential that you extensively train the welders on the job scope.
Besides substantial training, the best option for you should be to recruit welders who have experience working with TIG welding. There are so many aspects that the welders need to maneuver simultaneously with perfect balance.
TIG welding requires high precision. Objects that require TIG welding need a minimum level of quality assurance. One or a few wrong steps in operation might lead to a severe loss of weld quality.
Compared to MIG welding, it might prove significantly more challenging to train your welders on TIG welding but never compromise on this factor. Indeed, you don’t want to risk the quality of the product damaging your business.
Between MIG And TIG, Which Process Is Easier For Applications?
Generally, there are specific kinds of applications where each particular type of welding is required. But if you compare, MIG welding is comparatively easier in applications than TIG welding due to the simplicity of the process.
If you perform MIG welding, you can position the weld-gun at the specific point where you want to complete the joint. The different stages of progression required to be performed simultaneously are automatically performed by the MIG weld-gun.
For example, the weld-gun rolls the spooler to supply the wire feed as programmed to balance the optimum conditions. The consumable wire is also positioned at the perfect location where applicable, so you don’t have to worry about manually adjusting the position. So, it’s pretty simple and convenient for the welder to complete the job.
On the other hand, during TIG welding applications, you have to feed the wire manually. You should take care that you provide not more or less, but just the balanced amount required. Moreover, you should also position the wire perfectly to secure the quality of welding.
Since you don’t need to maintain all these simultaneous parameters during the MIG welding, it’s much easier to perform than TIG welding.
How Does Laser Welding Compare To MIG And TIG Welding?
Laser welding is an entirely different type of welding process compared to MIG or TIG welding.
Both the MIG and TIG welding are arc welding because they use electric current to create an artificial arc to weld metals. On the other hand, in laser welding, you can use an appliance that produces a high-intensity laser to focus on the connection point.
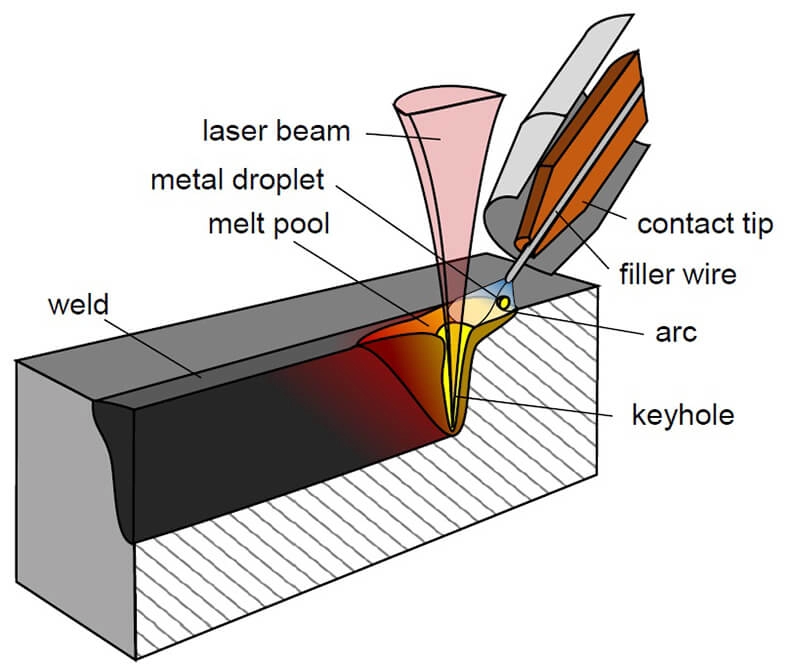
No arc is created here, but due to the high intensity of the laser ray, the surface material of the joining components quickly melts. When solidified, a bond is formed to seal the complete high-speed connection.
Does Both The MIG And TIG Welding Process Require Consumable Filler Material?
Whether or not you require consumable filler material depends on the type of process and the object you are working on. For MIG welding, it’s mandatory, while for TIG welding, it’s optional.

For MIG welding, the consumable filler material is mandatory since the filler material is used as the electrode in the feeding wire. This electrode acts as a conductor to pass the electricity. Simultaneously, the feeding wire is melted at the head following specific rates to form the weld pool.
For TIG welding, you can perform the welding operation with or without the filler material. When the workpieces comprise thinner sections, it is sufficient to work without the filler material. But if working on comparatively thicker sections and suggested by the technician, you can manually fee the filler material.
Is GMAW The Same As MIG?
There are common terms that many people get mixed up with. The fact is, both the GMAW and the MIG processes have similarities, but not wholly the same.
GMAW is an acronym that stands for gas metal arc welding. The basic of gas metal arc welding is that consumable wire is used as an electrode to conduct the electricity. This electrode simultaneously acts as the filler material at the weld pool.
This part is similar to that of MIG welding. But where’s the difference?
To understand that, you need to focus on the complete wider area of GMAW. Although the basic process is the same, MIG is just a sub-category within the GMAW process.
GMAW includes all the processes where the consumable wire electrode is used. There are many types under GMAW where further categorization is made on the type of shielding gas used. Sometimes inert gases are used as the shielding gas, while sometimes active gases are used with a mixture of inert gas or individually.
It can be put like this, MIG welding is also a GMAW process where only inert gases are used as the shielding gas.
How Can I Compare MIG And TIG In Terms Of Diversity Of Application Scopes?
To understand the diversity of application scopes, you must focus on the working principle first. In MIG welding, the electrode itself melts to form the filler material.
So, you must use a metal electrode similar to the object on which the weld is being performed. So, you have to change the electrode every time you are working on things with different metals.
In comparison, the filler material is not always mandatory in TIG welding since the electrode is non-consumable. It melts the primary metals of the object’s surface to form the connection. So, you can use the same appliance without changing it for a diverse set of applications.
Even when you are required to use filler material for specific objects, you don’t need to feed the material inside the machine and manually introduce it at the weld pool. This is extremely practical, especially when you are working on a complicated workpiece with diversity in multiple parts.
Another application scope is the joining of like metals. With MIG welding, you can only join like metals. But with TIG welding, you can join dissimilar metals.
Do I Need To Control The Intensity Of Welding In TIG And MIG Welding?
In MIG welding, most of the features are automatically controlled by the weld gun. So, you only have to worry about the connection point and the pace of welding.
Comparatively, for TIG welding, you have to manually control all the parameters like the flow of current, induction time to manage the welding intensity. Since the area of effect is too small, it can induce a tremendous amount of heat in a concentrated zone.
So, you have to control the amount of electricity supplied to control intensity so that targeted penetration levels are achieved. If it exceeds much or is lower than required, both will reduce the weld quality.
What’s The Difference Between MIG And MAG Welding?
MIG stands for Metal Inert Gas, and MAG stands for Metal Active Gas. You can understand the difference between them simply from the expressing terms.
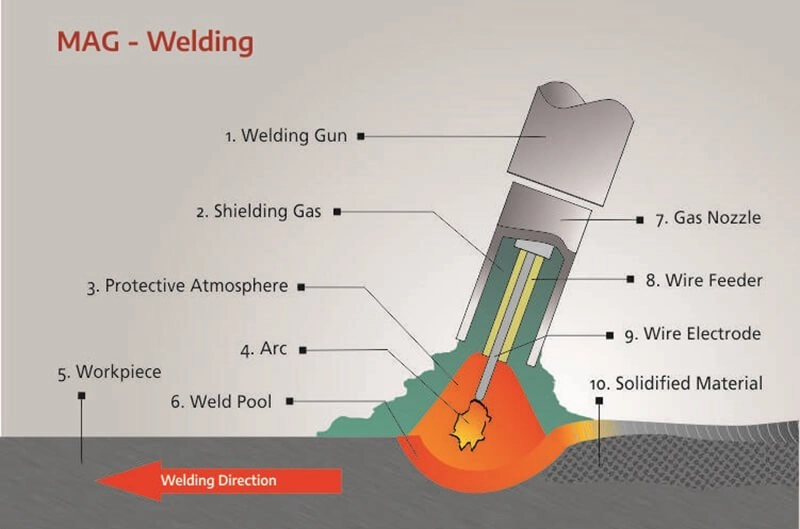
Both MIG and MAG are GMAW welding processes. In the MIG process, you have to supply external inert gases to act as the shielding gas, while in the MAG process, you have to supply a mixture of active gases like oxygen or carbon dioxide.
What Is GTAW?
The acronym GTAW stands for Gas Tungsten Arc Welding.
GTAW is basically another term used for TIG welding.
How Does The Cost Of MIG Welding Compare To The TIG Welding?
The MIG welding always costs less compared to TIG welding. But the cost-effectiveness doesn’t factor much due to the consumables, as the consumables of TIG are only slightly expensive than MIG welding.
The cost differences come due to the vast amount of time required in production by TIG welding. Practical estimates show that the time factor is almost double in TIG compared to MIG production.
What Materials Are Used To Prepare The Electrode In MIG And TIG Welding?
In MIG welding, the electrode is consumable and acts as the filler material to form the joint. So, you must choose the electrode similar to the parent material of the object you want to join.
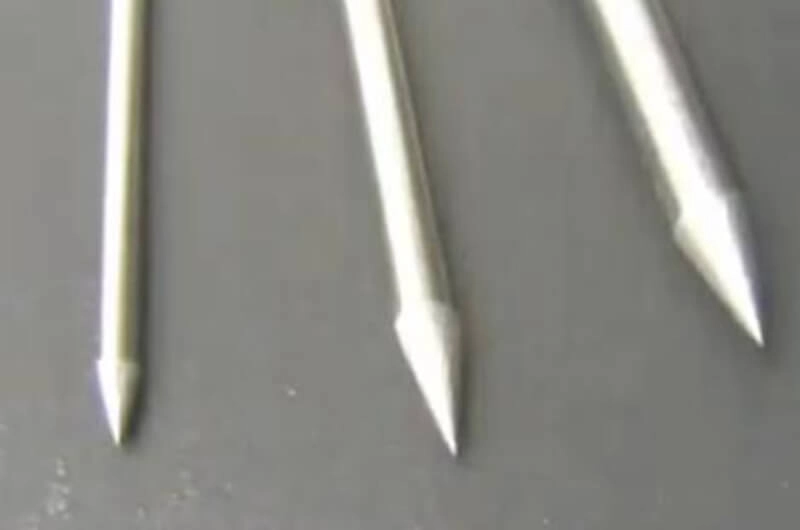

For TIG welding, the electrode is made of tungsten. This electrode is non-consumable if you use it properly.
Do I Need To Worry About Weld Spatter On MIG And TIG Welding?
Due to the large area of effect, the weld bead gets scattered during MIG welding. It’s hard to control, but with decent experience, you can keep the weld spatter to a minimum level.

In comparison, you can perform an aesthetically valuable welding operation with TIG welding as you don’t need to worry about weld spatters.
In What Kinds Of Welding Applications Can I Use The MIG Welding?
You can use MIG welding for various kinds of applications. The examples include:
- Farming Equipment
- Automobile and vehicle industries
- Railroad track manufacturing and repairing
- Metal sections repair
- Underwater welding developments
- Construction joints
- Pipe and tunneling joints
- Shipbuilding industries
In What Kinds Of Welding Applications Can I Use The TIG Welding?
You can use TIG welding in all the fields mentioned above, where MIG welding is applicable.
But the extra feature that you can obtain using the TIG welding is the high-quality output, superior aesthetics, ability to join dissimilar metals and applications where high durability is required.
For A Very Professional Outcome, Which Welding Process Should I Choose Between The TIG And MIG?
The TIG welding process sacrifices speed operation to provide a better quality welding in terms of all the possible aspects compared to MIG welding.
So, if you target to achieve a superior and professional outcome, you should always choose TIG welding wherever applicable.
What Kinds Of Shield Gas Is Supplied During The TIG And The MIG Welding Process?
For both the welding operations, inert gas is supplied, which acts as the shielding agent.
Due to the non-reactive nature of inert gases like argon, helium, nitrogen, it doesn’t react with the newly produced hot welding bead. Moreover, it protects the welding surface to direct contact with the environment, preventing oxidation and other reactions.
What Is The Process Of Feeding Filler Wire In TIG Welding Compare With MIG Welding?
In MIG welding, the filler wire is automatically fed through the weld gun.
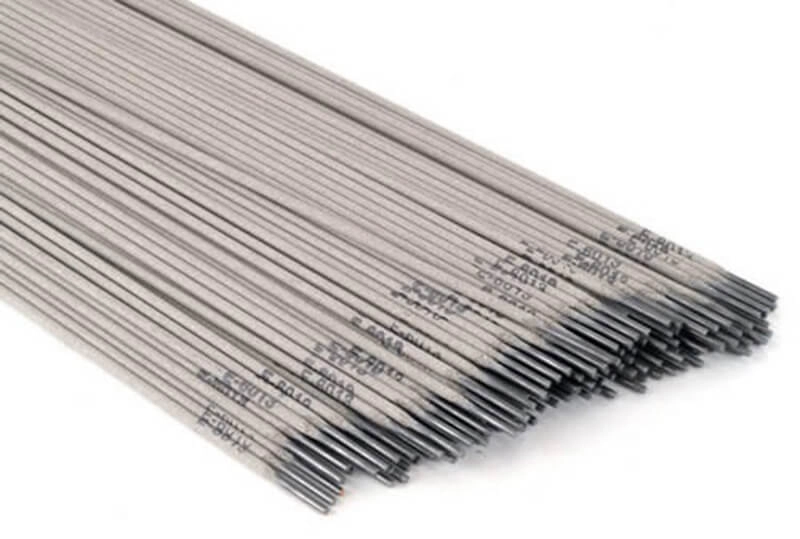

During TIG welding operation, can continue welding without filler wire for suitable cases. But if required, you can feed the filler wire manually by dipping the wire-head in the weld-pool during the welding process.
What Kind Of Welding Process Is Suitable For Working On Extremely Thicker Workpieces?
In the TIG welding process, the joining is achieved by directly melting at the surface of the base materials. So, it’s impractical to work on thicker workpieces.
In MIG welding, extra filler material is melted with the base material at the weld pool to create a combined joint. So, if you are working on exceptionally thick metal, it’s better to use MIG welding.
Can I Use TIG Welding To Join Non-similar Materials?
Yes, you can.
In the TIG welding process, the melted arc is generated by the joining object’s melted base metals, not primarily by filler material. The high-intensity concentrated force melts all the types of metals at the joining point.
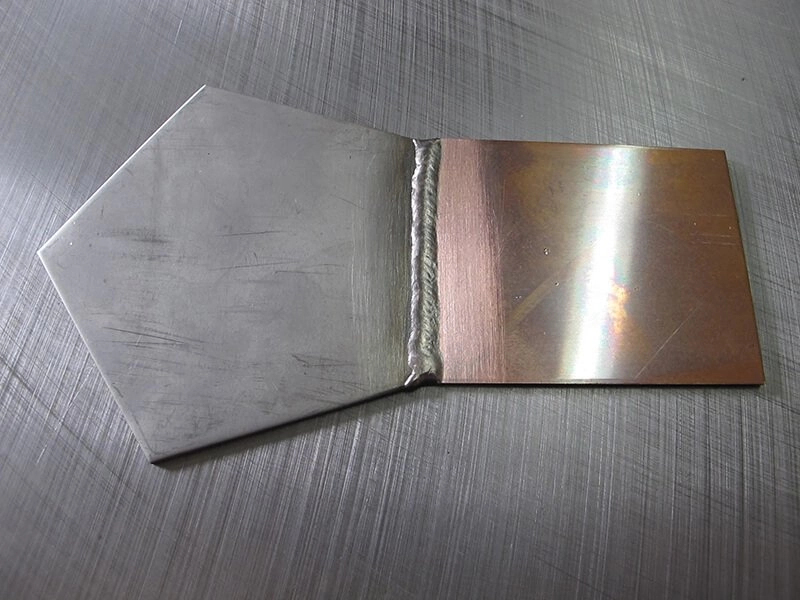

It doesn’t depend on whether you are joining like metals or non-similar metals. So, you don’t have to be worried about joining non-similar metals with the TIG welding.