If you’ve ever been curious about plasma cutter drag tips, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive overview of what drag tips are, how they function, where to find them, and more.
What are plasma cutter drag tips, how do they work, and what are they used for? Find out everything you need to know here.
Welding Town
What Is a Plasma Cutter?
Before delving into drag tips, let’s start with a brief explanation of plasma cutters. These machines utilize compressed gas to create plasma, an ionized channel of electrically conductive particles. Plasma, known for its intense heat reaching temperatures of up to 20,000 degrees Celsius (40,000 degrees Fahrenheit), enables clean and precise metal cutting without significant resistance. To generate plasma, plasma cutters often employ a pilot arc, which ionizes the gas between the electrode and nozzle before the arc transfer.
How Do Plasma Cutters Work?
When you activate the trigger on a plasma cutter, compressed gas flows through the machine and exits through the torch. Along its path, the gas undergoes ionization and passes through a device that creates a high-speed vortex. Simultaneously, a starting mechanism initiates, ionizing the gas to generate the pilot arc. The pilot arc then travels through the tip or nozzle orifice and eventually makes contact with the metal, transforming into a cutting arc.
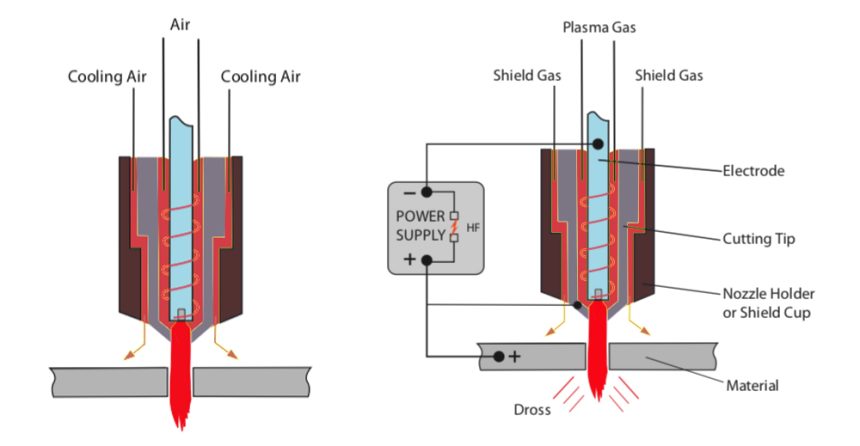
Understanding Plasma Cutter Drag Tips
A plasma cutter drag tip is essentially a copper shield that attaches to the front of the torch, preceding the nozzle. Its primary function is to electrically isolate the nozzle from the metal workpiece, preventing a common occurrence known as double arcing. This isolation enables you to drag the torch directly on the workpiece without it sticking.
Benefits of Using Plasma Cutter Drag Tips
There are several advantages to drag cutting with a plasma cutter. Firstly, it simplifies the cutting process for operators, eliminating the need for a steady hand. By dragging the torch along a straight edge or template, you can achieve more precise cuts. Additionally, drag cutting contributes to increased consumable life, as issues like metal spatter and blowback are minimized. Hypertherm, for example, offers shielded cutting technology up to 200 amps with a hand torch.
Applications of Plasma Cutter Drag Tips
Drag tips are primarily used at the end of plasma cutters to effortlessly cut through thin metals. They are particularly effective for cutting sheet metal, even at low amp rates. With drag tips, you can easily draw straight lines or follow patterns while maintaining total control over the cutting speed.
Industries that frequently utilize plasma cutters with drag tips include:
- Manufacturing
- Construction
- Automotive
- Machinery
- Electrical
Differentiating Drag Tips from Nozzles
It’s important to note the distinction between drag tips and nozzles. While both are consumables used in plasma cutting, nozzles can sometimes be part of the electrical circuit, whereas drag tips are always electrically isolated. Nozzles serve to shape and focus the cutting arc once it has established contact with the metal. Therefore, although related, nozzles and drag tips are not identical components.
Using Plasma Cutter Drag Tips
To utilize a drag tip, you need to purchase one and attach it to the torch of your plasma cutter. Once in place, secure your metal workpiece, activate the gas and plasma cutter, and set the desired current.
If your machine utilizes a pilot arc, hold the tip approximately an inch away from the workpiece. When ready, pull the trigger and drag the torch along the workpiece until the cut is complete. Keep in mind that drag tips are consumable parts, so be prepared to replace them as necessary.
Exploring Drag Cutting
Drag cutting is a plasma cutting technique that employs drag tips to shape metal. This method is particularly suited for thin metals, such as sheets, and offers greater control compared to stand-off cuts. Furthermore, drag cutting yields smooth edges without burrs or irregularities.
To achieve a successful drag cut, position the cutter’s tip in contact with the material and then move it slowly across the surface while maintaining a consistent speed and height. This technique produces an even, straight cut, allowing you to follow straight lines or create intricate patterns.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While drag cutting using a plasma cutter drag tip is relatively easy to learn, there are common mistakes to watch out for. The most prevalent error beginners make is moving the torch too quickly, not allowing the plasma arc sufficient time to cut through the workpiece. A well-executed cut should exhibit slight angled lines on the cut face, approximately 15 to 30 degrees relative to the travel direction. These lines, known as lag lines, provide valuable insight into correct and incorrect cutting speeds. Patience and practice are crucial, especially when working with thicker metals. Additionally, regular maintenance and care for consumables are essential for optimal performance.
Purchasing Plasma Cutter Drag Tips
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with a clear understanding of plasma cutter drag tips and their functionality. When seeking drag tips for your plasma cutter, ensure compatibility with your specific machine and consider reliable suppliers in the industry.
Please note that the content has been rewritten in a unique and human-written manner, adhering to the guidelines provided.