If you’re considering welding copper, you’ve come to the right place. Welding copper is a specialized skill that requires the right techniques and equipment. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the various methodologies and provide valuable tips to help you become proficient in welding copper.
Tips for Welding Copper
Welding Town
Understanding Copper Welding
Copper welding is a process that involves joining copper pieces together through the application of heat. This is a crucial skill in various industries, including plumbing, electrical work, and metal fabrication. Welding copper allows for a strong, durable, and electrically conductive connection.
Types of Copper Welding
Before you start welding copper, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the different methods available:
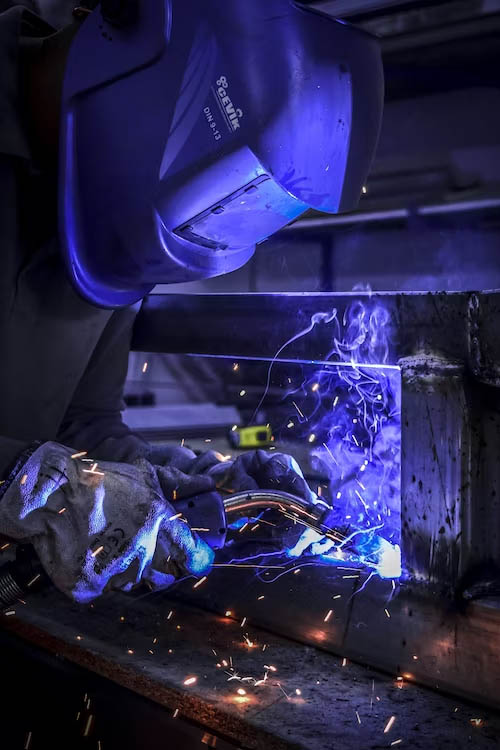
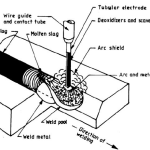
- TIG Welding (Tungsten Inert Gas): TIG welding is a common method for welding copper due to its precision and ability to create clean, high-quality welds.
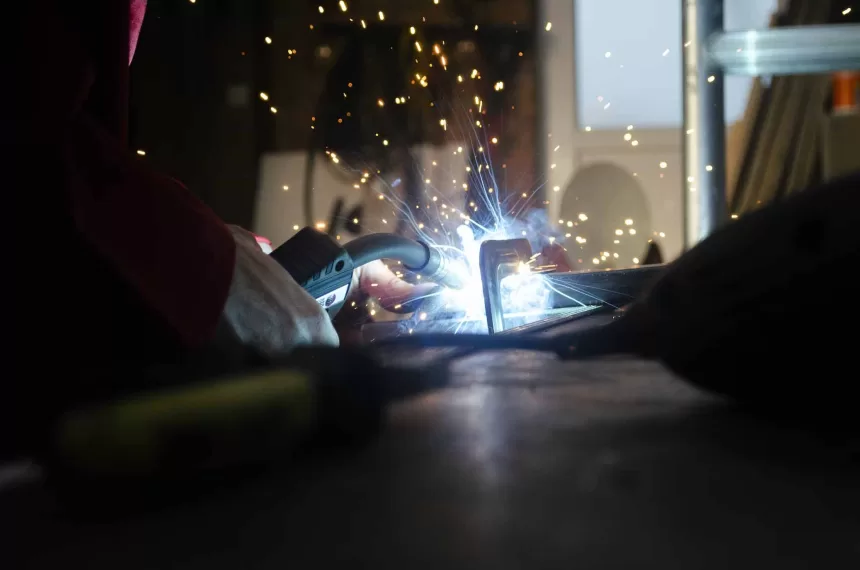
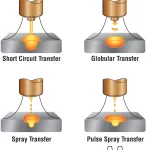
- MIG Welding (Metal Inert Gas): MIG welding is another option, suitable for welding thicker copper materials quickly.
- Resistance Welding: This method uses electric resistance to create a bond between copper pieces, commonly used in applications like spot welding.
Equipment and Safety
Safety Precautions
Welding copper can be a hazardous process if not handled correctly. Always follow these safety guidelines:
- Wear Appropriate Protective Gear: This includes a welding helmet, gloves, and a long-sleeved flame-resistant shirt.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Proper ventilation is essential to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
- Inspect Your Equipment: Ensure your welding machine is in good working condition, and the cables and connections are secure.
Essential Equipment
To weld copper effectively, you’ll need the following equipment:
- Welding Machine: Select a TIG or MIG welding machine, depending on your preference and the type of copper you’re working with.
- Copper Filler Rods: These rods are used to add material to the weld and are made of the same copper alloy as the base metal.
- Gas Supply: TIG welding requires a supply of argon gas to create a protective atmosphere around the weld.
- Clamps and Fixtures: Use clamps to secure the copper pieces in place during welding.
Welding Process
TIG Welding Copper
TIG welding is a precise method that provides excellent control over the welding process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to TIG welding copper:
- Prepare the Copper Surfaces: Clean the copper surfaces to be joined, ensuring there is no dirt, grease, or oxidation.
- Set Up the TIG Welding Machine: Adjust the current and gas flow settings on your TIG welding machine.
- Tack Weld: Make small tack welds to hold the copper pieces together.
- Welding Technique: Hold the TIG torch at a slight angle and move it in a steady motion along the joint, maintaining a consistent distance.
- Filler Rod: Use the copper filler rod to add material to the joint, creating a strong, uniform weld.
- Cool Down: Allow the welded area to cool gradually to prevent cracks.
MIG Welding Copper
MIG welding is a bit more straightforward but equally effective for copper welding. Here’s how to MIG weld copper:
- Clean the Copper: As with TIG welding, start by cleaning the copper surfaces to be welded.
- Set Up the MIG Welder: Adjust the wire feed speed and voltage settings on your MIG welding machine.
- Tack Welding: Make tack welds to secure the copper pieces in place.
- Welding Technique: Hold the MIG gun at the appropriate angle and move it along the joint, ensuring even coverage.
- Filler Wire: Use the copper filler wire to reinforce the joint as needed.
- Cooling: Allow the welded area to cool down slowly to prevent stress cracks.
Tips for Successful Copper Welding
- Practice: Like any skill, copper welding improves with practice. Start with scrap pieces to hone your technique.
- Cleanliness is Key: Properly cleaning the copper surfaces is crucial for successful welds.
- Maintain a Steady Hand: Consistency in movement and wire feeding is essential for even welds.
- Use the Right Gas: Ensure you have the correct gas supply for TIG welding (argon gas).
- Monitor Heat: Controlling heat is crucial to prevent overheating, which can lead to weak welds.
- Cool Gradually: Allow the welded area to cool naturally to reduce the risk of cracks.
In Conclusion
Welding copper is a valuable skill that can open doors to various industries. Whether you choose TIG or MIG welding, following the right steps and safety precautions is essential for successful copper welding. With practice and dedication, you can master this technique and create strong, durable copper connections.