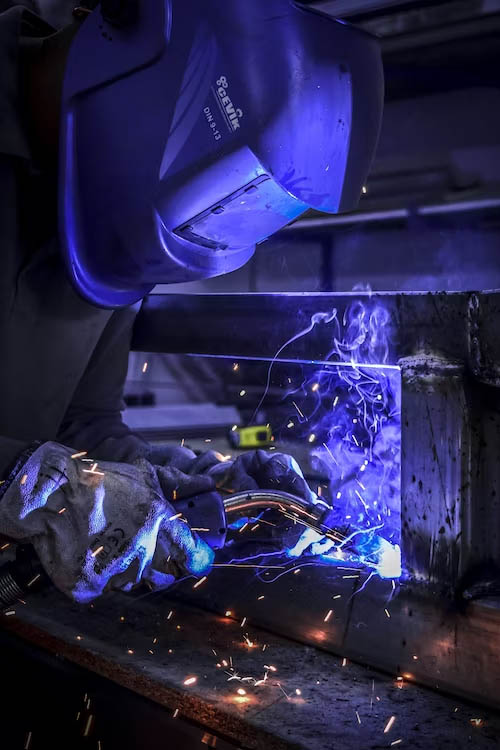
The temperature of the sun’s surface is approximately 5,505 degrees Celsius. The temperature of the earth’s core is approximately 5,982 degrees Celsius. Can you imagine how hot is a plasma cutter?
How Hot Is A Plasma Cutter?
Welding Town
Well, plasma cutter temperature can reach a staggering 25,000 degrees Celsius! That is more than anything you have ever come close to.
Are you curious about how this much heat is harnessed to cut some of the strongest metals like a hot knife is cutting through butter? Let’s dive deep into the fourth state of matter and find some more info about plasma cutting.
What Is Plasma?
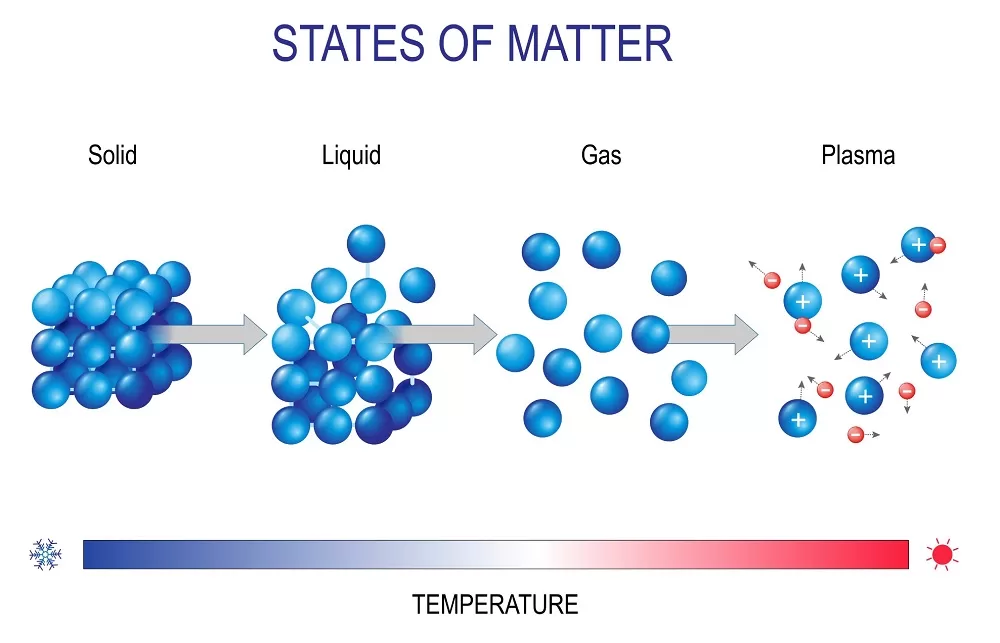
Plasma is often called the fourth state of matter. Till now, most of us might have learned about three states of matter, solid, liquid, and gas. But when a matter is superheated, it enters into the plasma state. Over 99% of the visible universe is comprised of plasma.
We often see plasma glow in the night sky. Yes, the stars, nebulas, and auroras you see are nothing but plasma. Even the lightning we see very often is also hot plasma. And neon signs? That, too, is plasma. And the sun? Yes, the star of our solar system is also plasma.
But how is a plasma formed? To know this, you need to get back to the solid-state of matter. In this state, the molecules of matter are in their lowest energy form. Once the heat is applied to solid matter, molecules gain some energy and make themselves a bit flexible. This is the liquid state of matter.
When the energy input is more than that, the state changes into gas, where particles start free-flowing. But if the heat increases by a lot, the speed of these free-flowing molecules gets extremely high. It results in stronger collisions between atoms.
These stronger collisions will tear one or more electrons free from atoms. We all know atoms that are missing electrons are known as ions. Thus, the heated gas becomes a mixture of positively charged ions and negatively charged electrons. This mixture of ions and electrons in the gas is called plasma.
Though plasma is mostly a natural state of matter, humans create plasma for different purposes. It is created by adding extra energy to a gas. Some types of fluorescent lights make plasma. Neon signs we commonly see in our cities also use plasma. Even some modern televisions use plasma, as well.
What is Plasma Cutting?
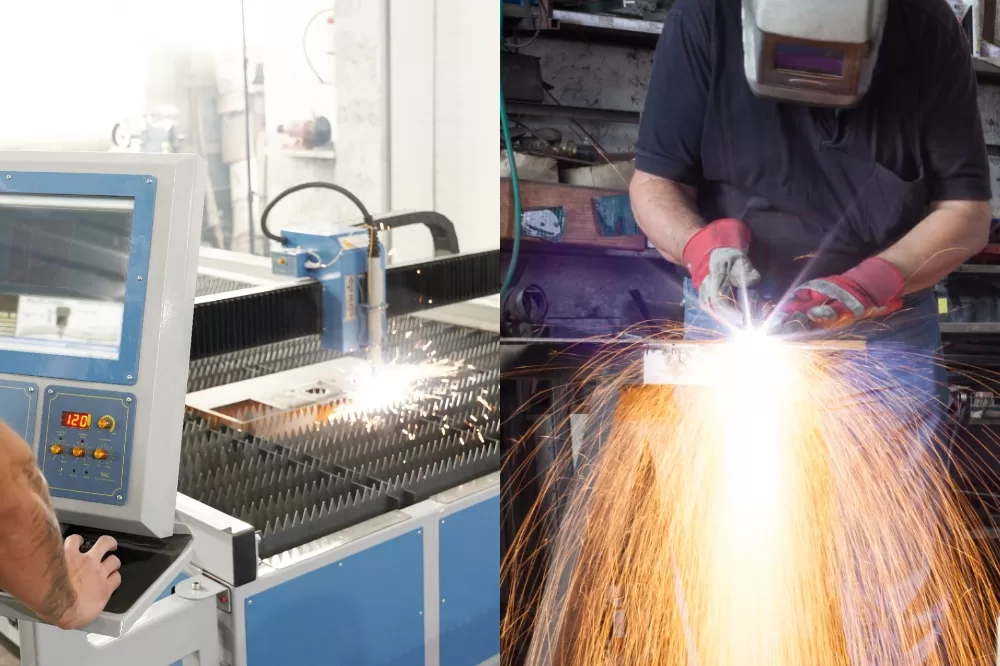

Plasma arc cutting or more commonly known as plasma cutting, is a procedure to cut materials where ionized gas in accelerated form is used to slice through materials that conduct electricity. This method of cutting is commonly used in fabrication shops, automotive repair, construction, salvage operations.
Plasma arcs can cut a wide range of electrically conductive metal materials. These include aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, nickel, titanium, etc. This process is very useful where oxy-fuel cutting isn’t that effective. Plasma cutting can also be performed underwater.
How Does a Plasma Cutter Work?
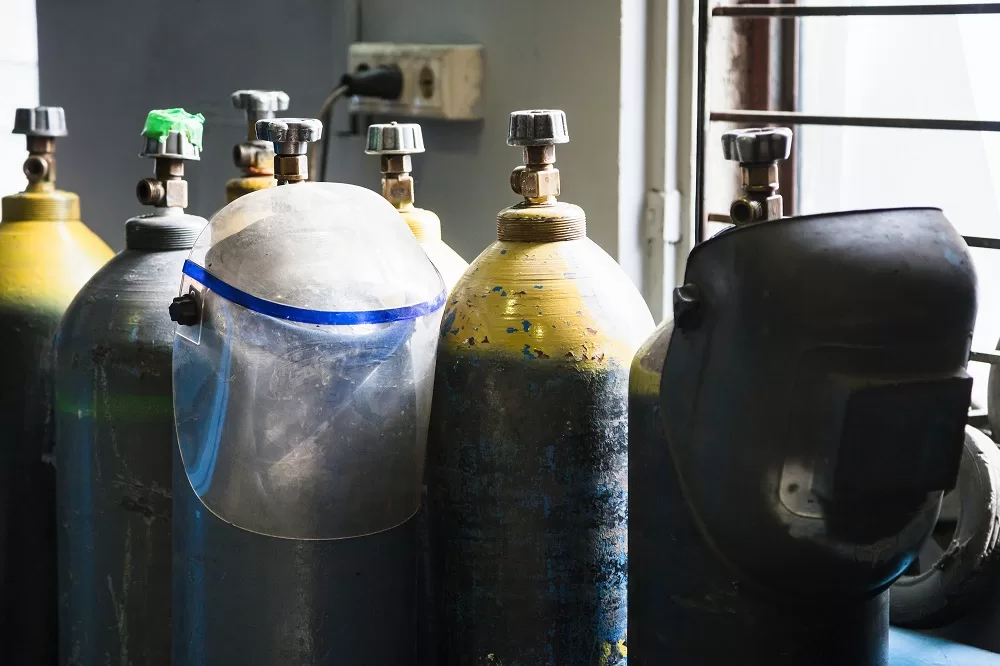

You might have seen gigantic robotic arms holding plasma cutters on a big work table where metal sheets are cut with ultimate precision. There are also uses of handheld plasma cutters that are of low cost and high performance. To know a plasma cutter inside out, read this.
No matter what the size and shape of the plasma cutter are, they all work based on the same principle. The principle here is to send a pressurized gas like nitrogen, argon, or oxygen through a small channel. A negatively charged electrode lies in the center of the channel.
Once the power is applied to the negative electrode and the workpiece is touched by the tip of the plasma torch, a powerful spark is generated. Inert gases passing through the channel get heated up to a large extent where they change their state into the plasma.
A column of plasma is generated in this way with a temperature of approximately 17,000 degrees Celsius. This plasma cutter jet hits the workpiece. Where the column touches the metal workpiece, the energy of the plasma is transferred to the metal in the form of intense heat.
In this heat, the metal is melted in a fraction of seconds and the plasma jet moving at about 20,000 fps ejects the cut metal from the original piece. As long as the power supply continues and the plasma is in contact with the metal, the cutting process continues.
So that the contact between the plasma torch and the metal piece remains as it is, a shielding gas is used in this process. The shield also protects the cut from oxidation. The second set of channels in the plasma cutter releases this shielding gas around the cutting area. This gas also determines the cutting radius of the plasma jet.
What Gas Is Used In A Plasma Cutter?
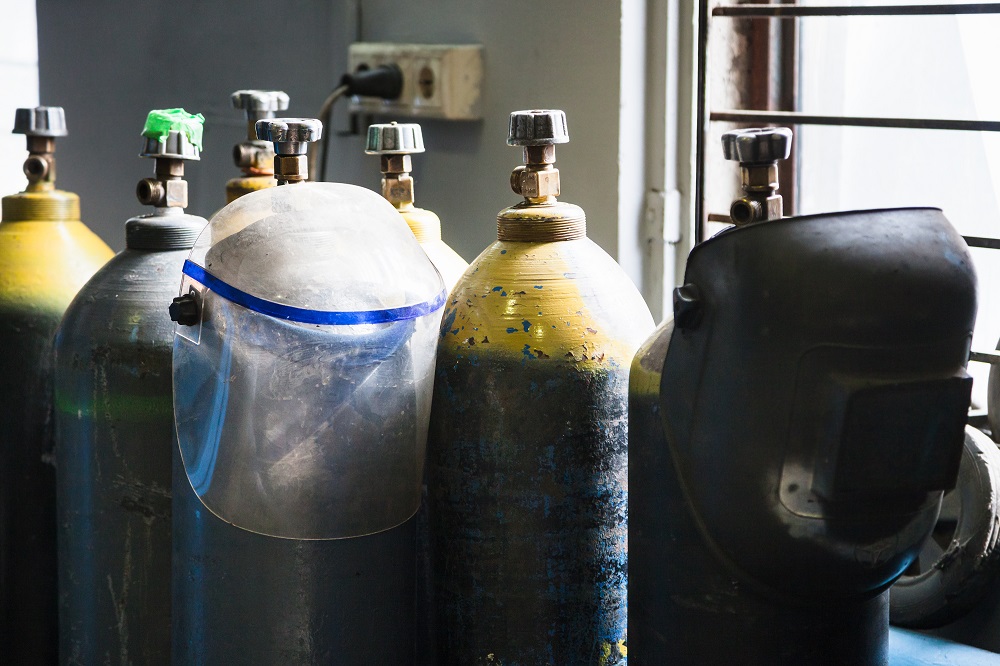

A plasma cutter is a crucial component of the cutting process. But without the right gas in the channels to heat up and form plasma, the cutting performance won’t be satisfactory. So, let’s get to know which gases are suitable for use in a plasma cutter.
Five gases are most commonly used in plasma cutters. These are compressed air, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, and argon. Usually, an individual gas is used in plasma cutters for thinner materials of less than half an inch.
But for thicker material, a suitable combination of these gases is used to improve the performance. Not only the thickness of the sheet is the considering factor here, but the chemical properties of the metal also need to be considered while selecting the gas for the plasma cutter. Here is a bit of a detailed discussion about these gases.
Compressed Air
Air that we breathe is the most inexpensive and versatile gas to use in plasma cutters in lower current cutting. This gas can be used on various metals like mild steel, sheet metal, stainless steel, aluminum, etc. Storing compressed air is also easier than other gases mentioned above. But the main problem with using compressed air is it can leave the cut area prone to oxidation.
Oxygen
Oxygen is a better option for having clean cuts on mild steel. Though this is not recommended for cutting stainless steel or aluminum, it can cut through carbon steel smoothly up to 1-1/4 inches. But using oxygen as the cutting gas will increase the expenditure of your projects, especially if it’s too big.
Nitrogen
In higher current settings, nitrogen is the gas of choice. It is used for cutting sheets up to 3 inches thick. It is excellent for cutting many materials like mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. If the workpiece is thicker, a combination of nitrogen and compressed air works great.
The combination of nitrogen and carbon dioxide will help obtain a greater cutting speed and cleaner edges. Nitrogen is also a very cost-effective solution for plasma cutting.
Argon
Argon is an inert gas, as we all know. Due to its inertness, it is very rare in nature. So, using argon in a plasma cutter will increase the cost to a large extent. But argon is very effective for plasma cutting due to the stability of the arc. It also prevents welding pools from atmospheric contaminants.
Though argon is a high-performance gas for plasma cutters, it must be combined with a secondary gas to increase the conductivity.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a very good thermal conductor. It also has the characteristic of quickly cooling hot metal surfaces after the cut is made. So, hydrogen is an ideal choice for plasma cutting. It works great on materials like stainless steel, aluminum, etc.
But due to the low atomic weight of hydrogen, its kinetic energy is low too. So, it must be paired with a secondary gas to increase the intensity of the plasma cutting arc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Plasma cutters are still covered with mystery for many people. To answer some of your curiosities, we have incorporated this section. Check these out and see if they match your quests too.
Q1. Can I Cut Wood with A Plasma Cutter?
Ans. Unfortunately, you can’t cut wood with a plasma cutter. As wood isn’t electrically conductive, it can’t be cut with a plasma cutter. Plastic is also a common material that can’t be cut in this process.
Q2. Can a MIG Welder Be Used as A Plasma Cutter?
Ans. Yes, a MIG welder can be used as a plasma cutter. An air compressor and a carbon electrode will be required in this process.
Q3. Is Welding Possible with A Plasma Cutter?
Ans. Plasma cutter temperature is very high, so some might think of it as a way to join metal by melting. But the intensity of the heat of plasma just cuts through the metal at high speed. So, welding isn’t possible.
Final Word
Knowing how hot is a plasma cutter might be the first step for you in knowing plasma cutting better. We hope we could meet your quest throughout the post and ignite your curiosity like a plasma cutter ignites the gas mixture to reach a metal-blowing temperature.
Harnessing this much energy to use it in favor of mankind will always be a continuous endeavor for scientists across the globe. We hope this piece of information will be quite helpful for you to take future projects that include using a Plasma cutter.
Best of luck!