MIG welding is a popular and versatile welding technique used to join various metals together. While it is commonly associated with steel, MIG welding can also be used to weld aluminum. Welding aluminum requires a slightly different approach compared to welding steel due to the unique properties of the metal. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the steps of MIG welding aluminum, providing you with valuable tips and techniques to ensure successful welds.
How To MIG Weld Aluminum, A Home Welder Tips For Success
Welding Town
Section 1: Understanding Aluminum Welding
Aluminum possesses distinct characteristics that make it challenging to weld compared to other metals. It has a lower melting point and higher thermal conductivity, which affects the welding process. Before diving into the actual welding process, it is essential to understand the properties of aluminum and how they influence the welding technique.
Section 2: Preparing for Aluminum Welding
Proper preparation is crucial for achieving high-quality aluminum welds. This section will cover important steps such as cleaning the aluminum surface, selecting the right filler wire, and ensuring a suitable shielding gas. We will also discuss the importance of using a clean and well-maintained MIG welding machine specifically designed for aluminum welding.
Section 3: Setting Up the MIG Welding Equipment
To achieve optimal results when welding aluminum, the MIG welding equipment needs to be properly set up. This section will guide you through the process of selecting the appropriate wire size, adjusting the wire feed speed and voltage settings, and setting the gas flow rate. Understanding these settings is vital to ensure the integrity and strength of your welds.
Section 4: MIG Welding Techniques for Aluminum
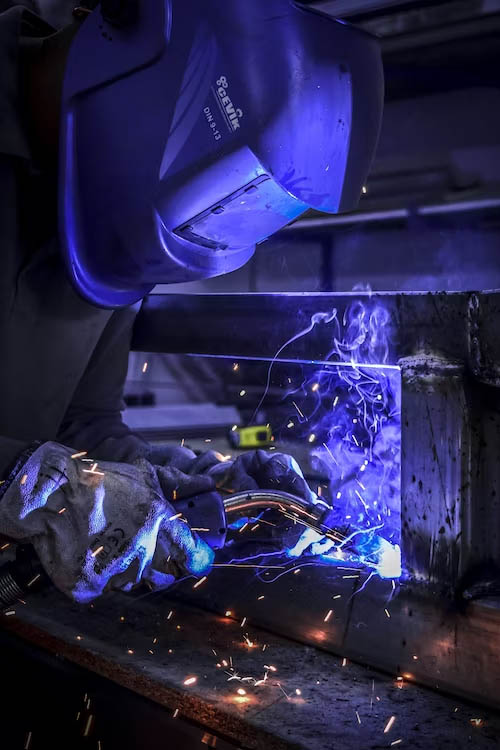
This section will delve into the actual MIG welding techniques used for welding aluminum. We will explore essential techniques such as gun angle, travel speed, and the push or pull technique. Additionally, we will provide tips on controlling heat input and avoiding common issues such as burn-through and distortion.
Section 5: Safety Considerations
Safety should always be a top priority when engaging in any welding activity. Welding aluminum comes with its specific hazards and safety considerations. In this section, we will cover the importance of proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and safe handling of the equipment. Following safety guidelines will help prevent accidents and ensure a secure working environment.
Section 6: Troubleshooting and Tips
Even with proper preparation and technique, challenges may arise during the aluminum welding process. This section will outline common problems encountered while MIG welding aluminum and provide troubleshooting tips to overcome them. From issues like poor penetration to porosity, we will equip you with the knowledge to address these challenges effectively.
Conclusion
MIG welding aluminum opens up a world of possibilities for joining this lightweight and versatile metal. By understanding the unique properties of aluminum, adequately preparing the welding area, and employing the right techniques, you can achieve strong and reliable welds. Remember to prioritize safety throughout the process and consult professional welders or experts if needed. With practice and perseverance, you can master the art of MIG welding aluminum and bring your metalworking projects to life.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of MIG Welding Aluminum
Advantages
- Can produce good quality welds with time and skill spent on preparation, the correct setup, and equipment.
- Able to weld 14 gauge to 1/4 inch Aluminum depending on the capabilities of your welder and preparation
- No need to buy a TIG welder and learn those skills and have that expense or pay an expert TIG welder to weld some Aluminum for you.
Disadvantages
- Needs practice around the correct setup of your MIG welder to weld well.
- Only have a home 115v or 140-volt welder then you’ll only be able to weld up to 1/8th of an inch thick Aluminum without needing a 220-volt welder. With a 220-volt welder, you can go up to 3/8th of an inch.
- 1/4 inch thick Aluminum will need pre-heating before welding.
- Particularly with an underpowered welder.
- Welding thinner than 18 gauge Aluminum needs a specialized setup
- Any other position other than flat or mild downhill horizontal is out. Overhead welding of Aluminum needs special skills.